Boost your team's skills and your budget! Enjoy group discounts for collaborative learning. Send an inquiry to info@peassociations.com.
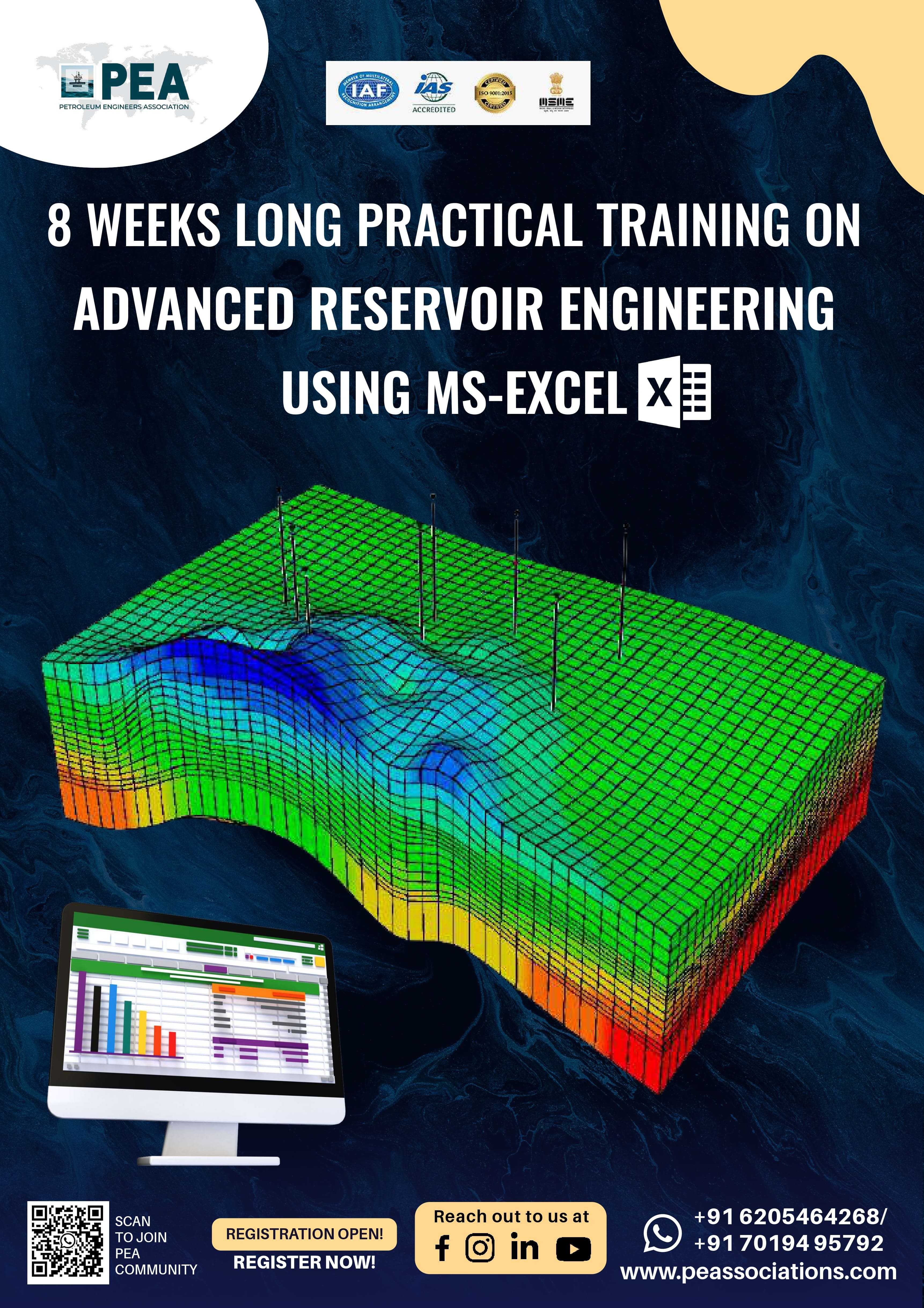
Integrated Production Modeling and Optimization
Description
This
provides an extensive and practical knowledge for understanding of the concepts
and practical applications of full field modelling including reservoir, pipe,
and surface network flow simulations. Analysis of the reservoir component is
critical for identifying the original resources (STOIIP and GIIP) and
understanding the main reservoir driving energies and mechanisms. Additionally,
reservoir modelling with material balance analysis can predict full field
performance. At the bottomhole terminal, the system must be solved for
appropriate operating point using inflow and outflow models. Recently, several
inflow and outflow models can be applied based on the field type and the
operating conditions. At surface, analysis of the production systems is
important for optimizing the field performance and maximizing the revenues.
Integrated network modeling offers this opportunity by full system analysis and
predict the possible bottlenecks. Accordingly, actions can be applied for
optimization and improvement. Network and field performance covers the
interactions of wells and pipelines and optimization of oil or gas flowrates
subject to constraints. When linked to reservoir models, the network model
becomes predictive with time allowing forecasting of production profiles,
timing changes of production and injection wells etc.
Integrated Production Modeling (IPM) is essential for optimizing the performance of oil and gas fields. In this course, participants will learn to seamlessly integrate reservoir, well, and surface facility modeling to enhance productivity. Leveraging industry-leading tools—MBAL for reservoir modeling, Prosper for well performance, and GAP for surface facilities—participants will develop a holistic approach to optimize production.
·
Explain the principles of reservoir fluid
composition, properties and modelling.
·
Explain the principle and limitations of the
material balance method and the influence of drive mechanisms on the recovery
factor
·
Build a material balance model for a new oil
field development
·
Evaluate the range of possible inflow and
outflow performance relationships for wells.
·
Applying the nodal analysis to predict well
performance and the effect of artificial lift
·
Build, validate, and match a naturally flowing
oil well model
·
Apply and interpret more complex inflow
modelling options
·
Run nodal analysis sensitivities, interpret the
results and export lift curves.
·
Perform history matching and run production
forecasts
·
Run a full field model with production
forecasting including producers and injectors
·
Analyze and optimize the surface production and
injection networks
·
Demonstrate proficiency in the use of production
optimization and modelling software
The course combines lectures, real-world case studies, and interactive hands-on sessions with IPM software. Each participant will work on exercises using MBAL, Prosper, and GAP, allowing them to gain practical experience under the guidance of industry experts.
·
Reservoir Engineers
·
Petroleum Engineers
·
Production Engineers
·
Field Engineers
·
Processing Engineers
Day 1
·
Reservoir fluid and rock systems
·
Integrated production system
·
Field development stages
·
Overall system approach
·
Methodology of pressure
loss in the wellbore
·
Importance of PVT data for
integrated production system analysis
·
Inflow performance models
Day 2
·
Reservoir to surface integrated modeling and
optimization
·
Material balance Theory
and applications
·
Material balance for oil reservoirs
·
Material balance for oil reservoirs (solving for
oil in place and aquifer size)
·
Summary of drive mechanisms as applied to
material balance
·
Linear form of MBE (Havlena & Odeh approach)
·
Straight-line analysis techniques
·
Analytical and graphical tools
·
Drive indices and energy plots
·
Dake & Campbell diagnostic plots, their
applications
·
Using material balance models for prediction
·
Analytical aquifer models – concepts
·
History
matching techniques (analytical and graphical)
Day 3
·
Material balance model:
·
PVT data and tank parameters
·
Aquifer models and rel-perms
·
Water influx models
·
Production and reservoir history
·
Prediction of reservoir performance
·
STOOIP calculation using Monte Carlo
·
Decline curve analysis - history matching and
prediction
·
Waterflood analysis with Buckley Leverett 1D
model
·
Simulation & Running a prediction
Day 4
·
Building a wellbore model
·
VLP flow correlations theory
·
Matching
PVT and flow correlations
·
Nodal analysis
·
IPR and skin models
·
Defining and matching well testing data
·
Flow regimes of the vertical and horizontal
pipes
·
Defining and matching the VLP model
·
Running sensitivities
·
Generation lift curves
Day 5
·
Importing VLPs and IPRs
·
Defining system constraints
·
Multi‐tank and multi‐PVT
·
Field development example
·
Well development schedule top meet target production profile
·
Well inflow models of horizontal, vertical,
deviated, multilayer and multilateral geometries
Day 6
·
Nodal Analysis calculations
·
Re-perforation studies, analysis of skin, the
application of sand control
·
Sensitivity analysis and prediction
·
Multiphase pressure drop models
·
Assessing the productivity of oil, gas and
condensate wells
Day 7
·
Flow assurance studies
·
Hydraulic investigations can be conducted on
flow regimes
·
Erosional velocities, superficial velocities,
and slug catcher sizing
·
Thermodynamic calculations can include studies
on hydrate formation, waxing, and salt precipitation
·
Hydrate and scale inhibition
Day 8
·
Multiphase network modeling and optimization
·
Integrated analysis for production and injection
networks
·
Field development planning, testing various
strategies, and forecasting
·
Prediction using a fixed oil rate
·
Prediction using a well model
·
Building a new oil reservoir model - optimizing
the production profile
·
Full field development planning
·
Assigning production constrains
·
Solving for the entire production network
·
Defining rule-based constrains
·
Case studies and field examples
On successful completion of this training course, PEA Certificate will be awarded to the delegates

Hesham Mokhtar is a Reservoir Engineering Team Leader at General Petroleum Company (GPC) in Egypt. He has extensive experience in reservoir management, characterization, and production optimization. He is skilled in using various software for reservoir simulation and analysis. He has also delivered training courses on waterflooding, PVT analysis, reservoir simulation, and more.
- 14+ years of Petroleum Engineering expertise delivering technical solutions to E&P portfolios.
- Expert in reservoir evaluations, log interpretations, and hydrocarbon estimations using tools like Techlog, Volumetric, DCA, MBE, OFM, and KAPPA
- Analyzes production data, material balance, RFT/MDT data, and pressure transients for reservoir performance and optimization.